# Intersection Observer API
看下下面的需求场景:
图片懒加载——当图片滚动到可见时才进行加载
内容无限滚动——也就是用户滚动到接近内容底部时直接加载更多,而无需用户操作翻页,给用户一种网页可以无限滚动的错觉
检测广告的曝光情况——为了计算广告收益,需要知道广告元素的曝光情况
在用户看见某个区域时执行任务或播放动画
之前为了实现上述功能,需要监听 scroll 事件并不断得调用 Element.getBoundingClientRect() 方法以获取相关元素的边界信息,这种方式可能会造成性能问题
所以Intersection Observer API提供了一种异步检测目标元素与祖先元素或 viewport 相交情况变化的方法,Intersection Observer API 允许你配置一个回调函数,当以下情况发生时会被调用:
每当目标(target)元素与设备视窗或者其他指定元素发生交集的时候执行。设备视窗或者其他元素我们称它为根元素或根(root)
Observer第一次监听目标元素的时候
# 使用
创建一个 intersection observer
let options = {
root: document.querySelector('#scrollArea'),
rootMargin: '0px',
threshold: 1.0
}
let callback =(entries, observer) => {
entries.forEach(entry => {
// Each entry describes an intersection change for one observed
// target element:
// entry.boundingClientRect
// entry.intersectionRatio
// entry.intersectionRect
// entry.isIntersecting
// entry.rootBounds
// entry.target
// entry.time
});
};
let observer = new IntersectionObserver(callback, options);
添加观察元素
let target = document.querySelector('#listItem');
observer.observe(target);
options 配置说明:
root: 指定根(root)元素,用于检查目标的可见性。必须是目标元素的父级元素。如果未指定或者为null,则默认为浏览器视窗rootMargin:根(root)元素的外边距。类似于 CSS 中的margin属性,比如 "10px 20px 30px 40px" (top, right, bottom, left)。可以理解为当观察者接近容器多远时就当做是进入容器区域了threshold:target元素和root元素相交程度达到该值的时候触发回调。粟子:想要
target元素在root元素中的可见性超过50%的时候触发回调,可以指定该属性值为0.5如果想要
target元素在root元素的可见程度每多 25% 就执行一次回调,那么你可以指定一个数组[0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1]
callback 返回参数说明:
entries [IntersectionObserverEntry 对象]:触发回调元素的信息,每个
IntersectionObserverEntry 对象包含以下属性boundingClientRect:目标元素的边界信息,同
Element.getBoundingClientRect()intersectionRatio:相交程度
intersectionRect:目标已进入区域的边界信息,相关于目标与
root元素的交集部分的boundingClientRectisIntersecting: 目标元素是否进入区域
rootBounds:
root元素的边界信息,同root元素.getBoundingClientRect()target: 当前目标元素
time:交叉被触发的时间的时间戳
observer:观察者的列表
# 实战例子
使用 Intersection Observer API 做的一个滚动索引列表
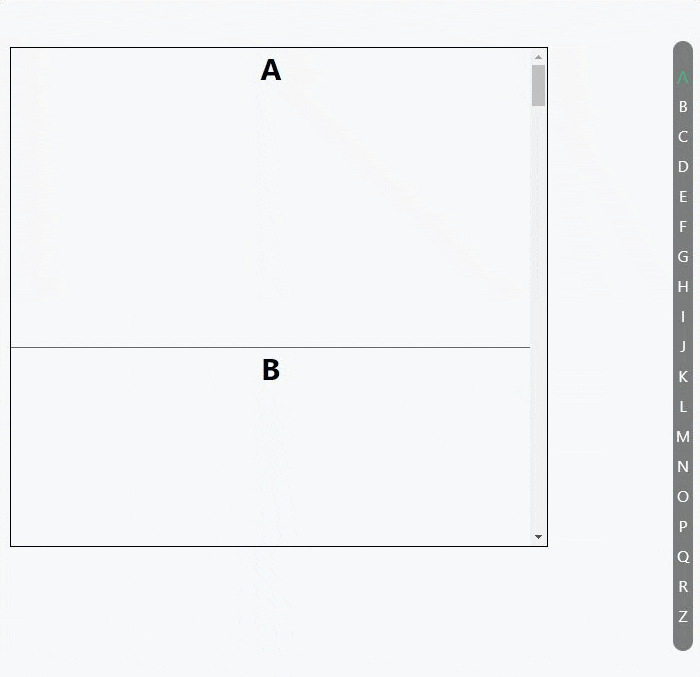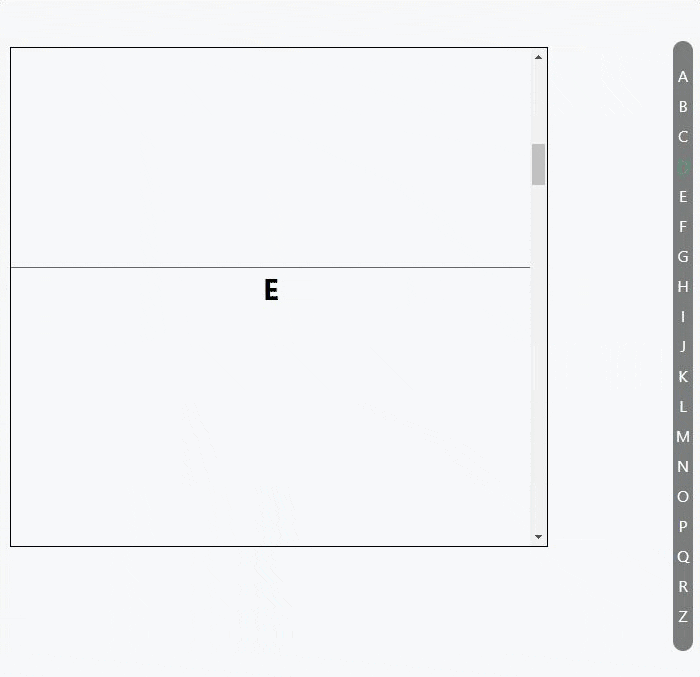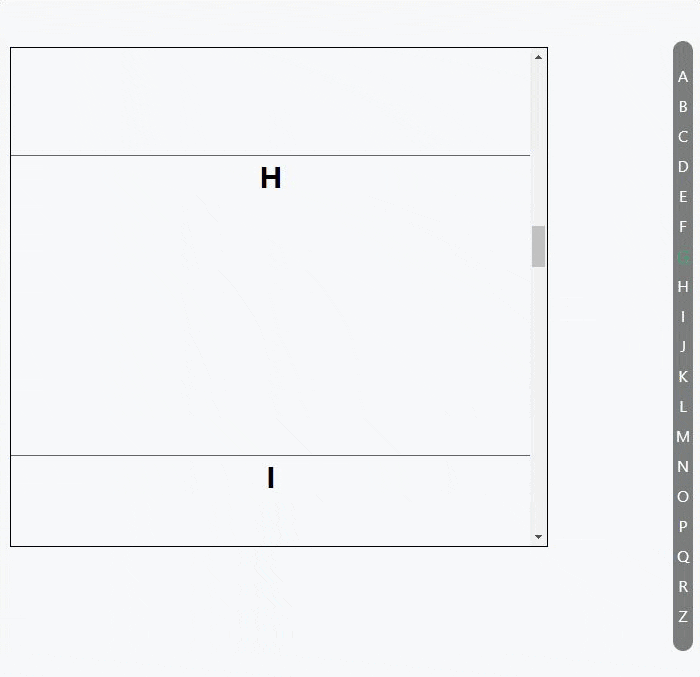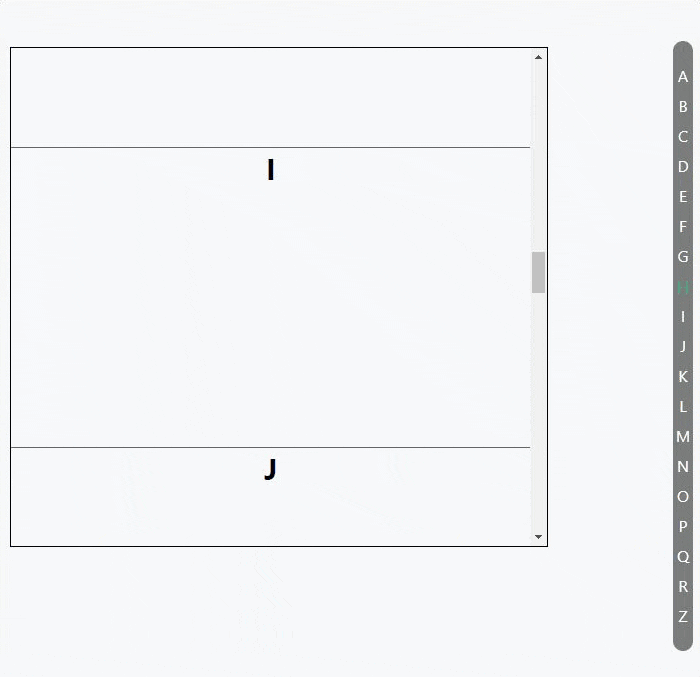
代码:
<template>
<div class="index-num">
<div v-for="i in list" :key="i" class="item" :class="{'act': act === i}">{{i}}</div>
</div>
<div class="scrollBox-box">
<div class="base" ref="scrollBox">
<div class="scrollBox" >
<div v-for="i in list" :key="i" class="item" :alias="i" ref="indexItem">
{{i}}
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "IndexList",
data(){
return {
list: ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'I', 'J', 'K', 'L', 'M', 'N', 'O', 'P', 'Q', 'R', 'Z'],
act: 'A'
}
},
methods: {
initInterSectionObserver(){
console.log('this.$refs.scrollBox', this.$refs.scrollBox)
if(this.interSectionInstance) return
let rootDom =this.$refs.scrollBox
let options = {
root: rootDom,
rootMargin: '0px',
threshold: 0,
}
let _this = this
this.interSectionInstance = new IntersectionObserver(function (entries, observer){
entries.forEach(entry => {
console.log('entry', entry)
if(entry.isIntersecting){
_this.act = entry.target.getAttribute('alias')
}
// Each entry describes an intersection change for one observed
// target element:
// entry.boundingClientRect
// entry.intersectionRatio
// entry.intersectionRect
// entry.isIntersecting
// entry.rootBounds
// entry.target
// entry.time
});
}, options);
(rootDom.querySelectorAll('.item')||[]).forEach(item => {
this.interSectionInstance.observe(item)
})
}
},
mounted() {
this.initInterSectionObserver()
}
}
</script>
<style scoped lang="scss">
.index-num{
position: fixed;
right: 10px;
top: 50%;
transform: translateY(-50%);
background: rgba(0,0,0,0.5);
width: 20px;
text-align: center;
color: #fff;
padding: 20px 0;
border-radius: 10px;
.item{
line-height: 30px;
}
.item.act{
color: #3eaf7c;
font-size: 19px;
}
}
.scrollBox-box{
width: 80%;
height: 500px;
position: relative;
margin-top: 70px;
.base{
//background: red;
height: 10px;
z-index: 2;
width: 100%;
position: absolute;
}
}
.scrollBox{
border: solid 1px #000;
overflow: auto;
position: absolute;
height: 500px;
width: 100%;
.item{
height: 300px;
font-size: 30px;
font-weight: bold;
text-align: center;
border-bottom: solid 1px #666;
}
}
</style>